What are Privacy-enhancing Technologies (PETs)?
In this era, information is the new currency, and privacy, together with data protection, has been elevated to global concerns. Between mass data breaches, invasive surveillance, and unauthorized data harvesting, we have all become uncomfortably aware of how our personal information is being collected, stored, analyzed, and abused. New technologies are rapidly emerging as companies and researchers introduce new tools to improve users’ privacy and data protection.
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) are a wide array of tools and methods that offer ways for companies to create products and services while ensuring data privacy.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
Definition: What are Privacy-Enhancing Technologies?
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) can be defined as:
“A group of methods and technologies (hardware and software solutions) for protecting individuals’ personal information while enabling data utility.”
The fundamental principle behind PETs is data processing without compromising user privacy. Using PETs, organizations can use, share, and analyze data to preserve the privacy of the individuals behind that data.
PET is not a single tool but comprises a broad category of approaches that include cryptographic techniques, anonymization methods, and architecture designs that reduce the amount of personal data exposure. However, their aim is to safeguard, ensuring that personal information remains private, even when used for data collaboration and analysis.
Goals of PETs
- Maximize data security by reducing the risk of data breaches or leaks.
- Prevent bad actors by rendering the data useless for malicious purposes.
- Facilitate safe data collaboration across departments and even organizations.
- Keep the consumers communications private from the company.
- Allow users to access data anonymously.
- Enable a company to use analytics and research to improve a product without gaining access to an individuals data.
Classification/Types of PETs
PETs are classified into the following types:
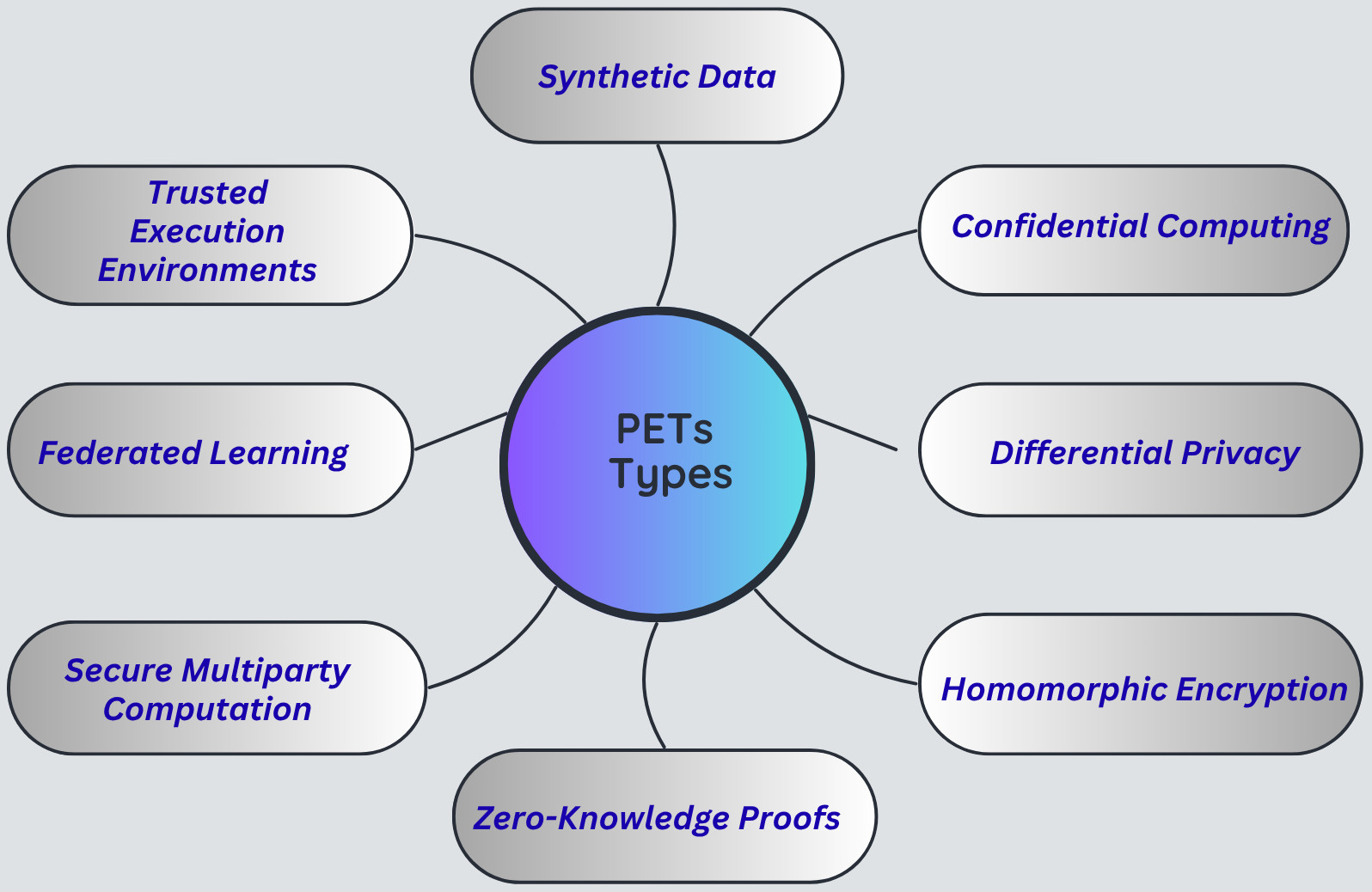
Synthetic data
Using synthetic data, organizations can generate artificial data that closely resembles real-world data while preserving privacy.
Synthetic datasets can mimic real data, encompassing the same shape and similar statistical qualities. While these datasets lack private details, they maintain correlations and patterns in real data. This way, companies can analyze and develop machine learning models without risking data exposure.
- A healthcare company uses synthetic patient data to test predictive disease diagnosis algorithms. This synthetic data will reflect the characteristics of real medical records, but actual patient information is not exposed. This way, privacy is protected, and at the same time, the algorithm is tested and refined.
- AI and machine learning often use synthetic data to create training datasets when real data is limited or too sensitive to use.
Confidential Computing
Confidential computing is an innovative approach that prevents unauthorized access to data during computation. It offers a new level of security in data processing and analysis.
Confidential computing uses two key data security methods, isolation and remote attestation. Isolation safeguards sensitive data while in use, while remote attestation verifies the protection of data and what it will be used for before starting computation.
- Confidential computing is used in cloud computing, wherein organizations can securely process sensitive data in the cloud without risking its exposure to the cloud provider or external threats.
- Banking institutions use confidential computing to collaborate and gain insights into cyber threats. This allows them to detect phishing campaigns, identify common patterns, and compare the phishing defenses of all participating organizations.
Differential Privacy
This is a mathematical technique used in data analysis. The differential privacy method introduces randomness or noise into query responses, making it challenging to pinpoint individual data points.
The differential privacy technique determines the precise noise needed for statistical privacy assurances. Not all noise-adding techniques are differential privacy methods.
Differential privacy preserves privacy by using aggregation to balance data analysis. It summarizes and generalizes data to derive meaningful insights while protecting individual privacy.
- Governments usually apply differential privacy to their census data, ensuring individuals cannot be identified through detailed demographic information, even when data is broken down into small geographic units.
- Companies can analyze customer behavior patterns across geographical regions or demographic groups without revealing any individuals data.
Homomorphic Encryption
This method enables computations on encrypted data without decrypting it first. In other words, meaningful operations are carried out on encrypted data, thus ensuring its privacy is intact.
- Companies use homomorphic encryption and perform data analysis on encrypted datasets without revealing the underlying sensitive information.
- Homomorphic encryption is used in the financial industry to perform calculations on encrypted transactions, ensuring that sensitive financial information remains protected and that no data breach occurs.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)
This method allows one party to prove to another that they possess certain information without exposing the information itself. This technique is useful for authentication and verification without disclosing sensitive information such as user credentials.
- Cryptocurrencies like Zcash utilize ZKPs to enable private transactions, where the sender, receiver, and transaction amount are hidden while still ensuring the transaction’s validity.
- ZKPs can be incorporated into online voting systems to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of votes. Voters can prove they cast a valid vote without revealing their chosen candidate.
Secure Multiparty Computation (SMC)
SMC relies on cryptographic protocols and uses encryption and mathematical techniques to enable multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their individual inputs while keeping those inputs private.
It ensures that parties only know the output of the computation and no other data, even in the case of participants who follow the protocol correctly but might attempt to learn additional information from the received data.
- SMC is used by multiple institutions to securely analyze combined datasets without revealing their individual data to each other.
- Businesses can collaborate on shared market analyses, pooling their data for better insights, while maintaining the confidentiality of their proprietary datasets.
Federated Learning
Federated learning is a decentralized machine learning approach. In this method, a model is trained across multiple decentralized devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. Only model updates (gradients) are communicated, preserving data privacy.
- Federated learning enables mobile devices to improve features like predictive text, image recognition, or voice assistants without sharing sensitive user data with a central server.
- Hospitals and healthcare institutions can collaborate on training AI models for medical diagnosis without exchanging sensitive patient data, preserving privacy while developing more robust models.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs)
TEEs are secure hardware or software environments within a computer system that are used for executing sensitive code or operations. TEEs protect code and data within them from external tampering, even from the operating system or other software layers.
Enclaves and trusted execution environments are key parts of TEEs and are broadly interchangeable terms. They typically imply that the environment is hardware-based. A few rare exceptions exist for software-based ” enclaves, ” but they provide less robust security.
- TEEs enable secure data processing in the cloud, where users can compute on sensitive data without exposing it to the cloud provider or other parties.
- TEEs are used in the finance industry to securely process transactions and other sensitive operations while protecting the underlying data.
Importance and Benefits of PETs
PETs enable secure data processing, maintain privacy, and ensure compliance with ever-evolving privacy regulations. Organizations using PETs benefit in the following ways:
Data Protection Compliance
Many firms use privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and others. PETs help organizations remain compliant by implementing privacy-by-design and privacy-by-default principles. Organizations are required to implement robust privacy protection measures for personal data, as these regulations become stricter globally and help organizations avoid legal consequences, penalties, and reputational damage.
Secure Data Collaboration
When organizations have their privacy policies in place, consumers are more willing to share their data. PETs help build trust by ensuring the data is handled transparently and securely.
Organizations also need to collaborate with third parties such as partners, vendors, or researchers. PETs allow for secure data collaboration by keeping sensitive information safe, promoting innovation and collaboration on data analysis.
Data Minimization
Data minimization, which dictates that only the minimum amount of data necessary for a specific purpose should be collected and processed, is the key principle of regulations like GDPR. PETs upheld this principle by helping organizations to work with data more securely and efficiently without storing or processing unnecessary personal information.
Data Misuse Prevention
PETs framework prevents data misuse. PETs apply techniques such as encryption, homomorphic encryption, and other privacy-preserving techniques to ensure data is only used for intended purposes and by authorized users. This reduces the risk of data misuse, selling, or sharing.
Innovation and Data Use
PETs enable data analysis and machine learning on encrypted or anonymized data, allowing innovation without violating privacy. With PETs, organizations can utilize data for analysis and insights without compromising their privacy. New opportunities for innovation can be unlocked while adhering to privacy standards.
Reduced Legal and Financial Consequences
Exposing personal data results in significant financial penalties and reputation damage to organizations. Using PETs can help mitigate the risk by ensuring that the data is handled securely and complies with privacy laws. The benefits discussed above are from the organization’s point of view. As for individuals, PETs provide the following benefits:
Enhanced Privacy
Users find it hard to maintain privacy as more personal data is shared online. PETs help individuals control the sharing of their personal information by retaining ownership and protecting their identities.
Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
Data breaches always pose a significant threat to personal privacy. Individuals can become victims of identity theft, fraud, or financial theft. PETs like differential privacy, encryption, and SMCs help minimize these risks, reducing the impact of potential data breaches.
Improved trust in digital platforms
Companies using PETs demonstrate their commitment to protecting user data, which improves trust in digital platforms.
Better online experiences
With PETs, individuals enjoy more personalized and engaging online experiences without sacrificing their privacy. Businesses can also offer tailored services and products while keeping personal information secure.
Real-World Examples of PETs
Here are the main applications of PETs:
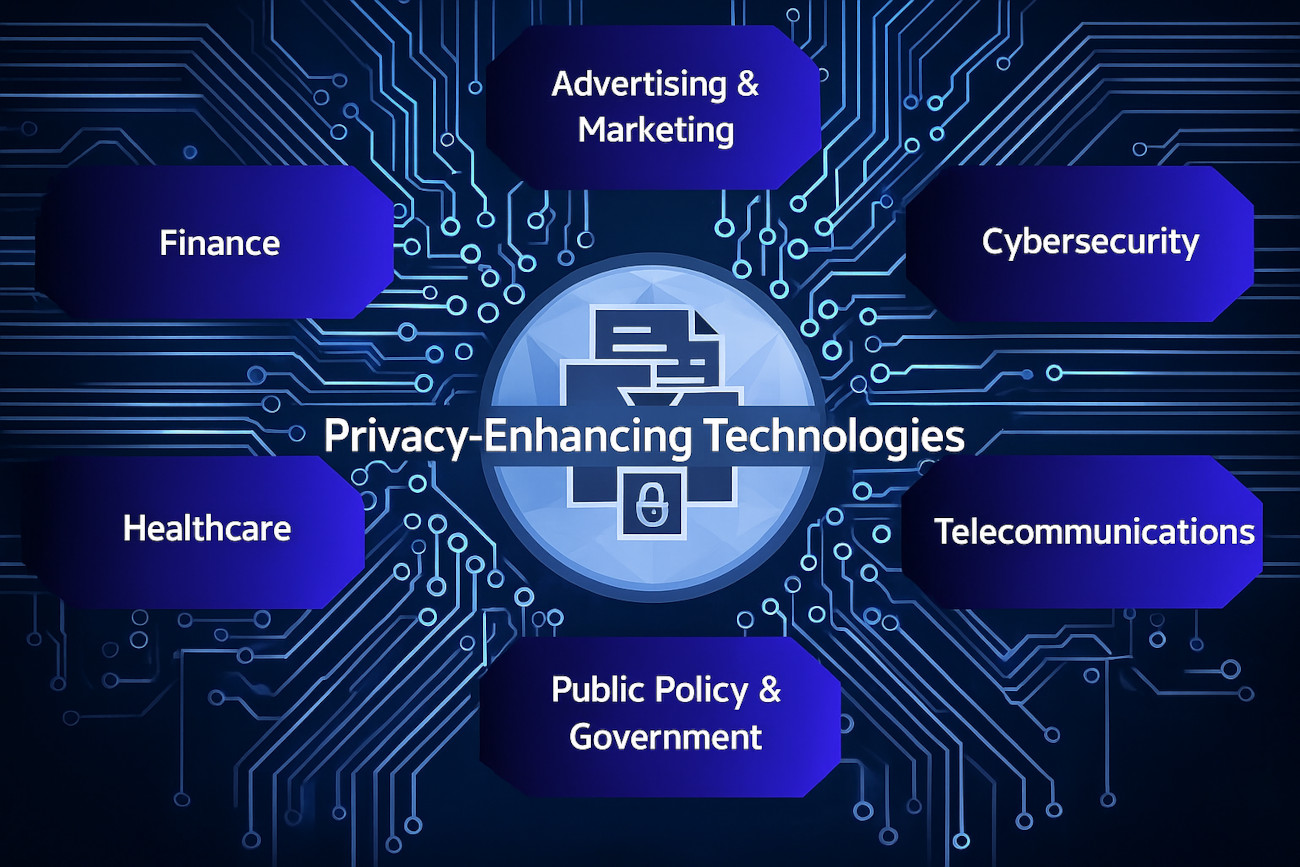
Healthcare
Medical institutions like hospitals and research centers use PETs like SMPC and federated learning to gain insights and collaborate without exposing patients personal information. For example, training AI models to test ER/PR (Estrogen/Progesterone receptor) algorithms for breast cancer detection using datasets from different hospitals.
Finance
Banks and other financial institutions use differential privacy and encryption methods to detect fraud and ensure compliance with regulations without compromising customer information. PETs help protect financial data during transactions, fraud detection, and risk assessment while adhering to regulatory requirements.
Advertising and Marketing
Companies collaborate with anonymized data to gain insights into market trends and consumer behavior while preserving individual privacy. PETs can also support privacy-compliant targeted advertising. For example, techniques like federated learning can be used to personalize ads without accessing user-level data.
Cybersecurity
PETs help detect threats, analyze network traffic, and protect sensitive data without exposing vulnerabilities. Organizations are increasingly adopting PETs to collaborate on threat intelligence and behavior analytics without sharing new data.
PETs methods play a critical role by ensuring that sensitive data remains protected even during processing, thus reducing the risk of insider threats or advanced persistent attacks. This behavior particularly helps in important sectors such as finance, defense, or telecommunications, where data breaches have far-reaching consequences.
Telecommunications
Telecom operators adopt PETs by using anonymization and pseudonymization to analyze usage patterns for network optimization to provide better reception without tracking user identities.
Public Policy and Government
PETs are utilized by public policy and government institutions to analyze census data or mobility trends without tracking individuals. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many contacts were traced using PETs to balance public health with privacy. Institutions also use PETs to meet data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA while maintaining operational efficiency. This allows businesses to extract valuable insights while upholding stringent privacy standards.
Challenges in Implementing PETs
- Complexity: Advanced PETs like homomorphic encryption or SMPC require specialized expertise as they are computationally intensive. PETs are complex, expensive, and resource-intensive to implement, which limits their accessibility to smaller organizations.
- Trade-off Between Utility and Privacy: Removing identifiers (anonymization) or adding noise (distinct privacy) can reduce the accuracy or usability of data for certain analyses or tasks.
- Standardization Issues: PETs lack unified universal implementation standards across industries, making integration and compliance more difficult.
- Performance Overhead: PETs such as federated learning or homomorphic encryption can introduce latency and require greater computational resources, introducing performance overhead.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: PETs operate within existing legal and regulatory standards, and their implementation must align with rapidly evolving requirements.
- Implementation and Expertise: Because PETs are relatively new, most organizations lack the necessary expertise to implement and manage them effectively.
- Scalability: Using PETs across large datasets efficiently and cost-effectively is a significant challenge.
- Risk of False Sense of Security: Sometimes organizations over-rely on PETs without addressing the underlying issues of data governance and usage. This can create a false sense of security and potentially encourage harmful practices.
The Role of PETs in Artificial Intelligence
- Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning: AI uses PETs like federated learning and differential privacy to train models without compromising data confidentiality.
- Explainability and Fairness: PETs contribute to explainable AI by helping AI isolate and audit decisions while maintaining data protection.
- Bias Mitigation: Diverse datasets often restricted due to privacy laws can be included by anonymizing or encrypting them, enabling broader model training.
Future of PETs
PETs are rapidly evolving, and their importance will likely grow as data becomes more critical and regulations more stringent.
- Increased Standardization: ISO, IEEE, and NIST are attempting to create global standards for PETs that will help improve interoperability and adoption.
- Integration into Cloud Platforms: Prominent cloud providers are incorporating PETs natively, offering them as services like AWS Nitro Enclaves.
- PETs-as-a-Service: PETs are also bundled into APIs and SDKs so that smaller organizations can adopt them without in-house expertise.
- Quantum-Resilient PETs: Cryptographic PETs must adapt to quantum computing to remain secure.
- Cross-border Data Collaboration: PETs will be crucial in enabling international data partnerships as traditional data sharing becomes legally or ethically prohibitive.
Conclusion
PETs are foundational enablers of secure innovation in a privacy-conscious world. PETs offer a transformative approach that balances the needs of individuals, organizations, and regulators by embedding privacy directly into the tools and systems used to process data.
Adoption and advancement of PETs are necessary as the digital economy continues to evolve and AI and big data become more embedded in our daily lives. PETs are not only technological necessities but also a societal imperative to ensure that progress does not come at the cost of individual rights and privacy.
|
|
