Edge Computing: Top Use Cases
In this modern digital era, data generation is growing exponentially, and low-latency data processing has become a critical requirement. To cope with this exponential data growth, edge computing has emerged as a transformative technology. Edge computing processes data closer to where it is generated, thus bridging the gap between data sources and centralized cloud computing systems.
You can view edge computing as a distributed computing network that processes data close to its location and brings storage capabilities closer to where it is required. Edge computing minimizes latency, reduces bandwidth usage, and improves real-time decision-making.
In this article, we will understand the concept of edge computing and explore its top use cases, showcasing its applications across industries from autonomous vehicles and smart cities to manufacturing and healthcare industries.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
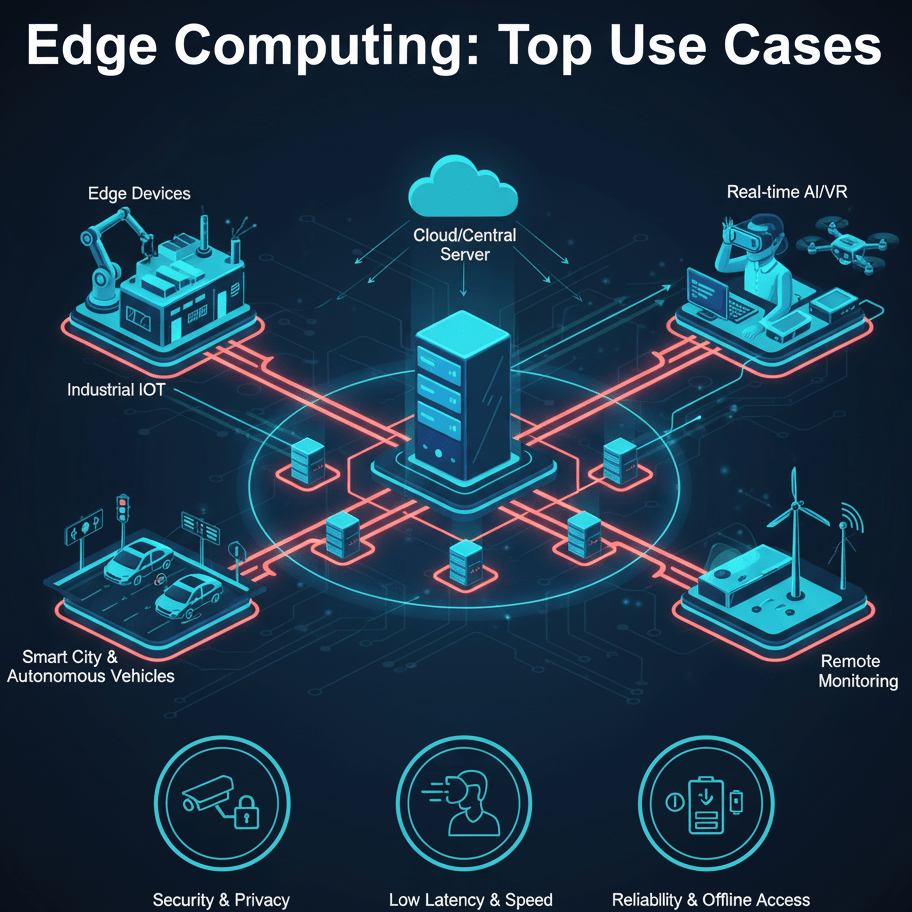
What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing Definition
Edge computing is the practice of processing and computing client data closer to the data source rather than on a centralized server or a cloud-based location.
Edge computing brings enterprise applications, data storage, and computing resources closer to where people consume the information, not to some centralized server or remote cloud location.
In edge computing, the computing resources, such as processing power, storage, and intelligence, are deployed at the “edge” of the network, near the data source. This is unlike traditional cloud computing, where data is sent to centralized servers for processing. In edge computing, computation is close to end devices, be it sensors, smartphones, or autonomous devices. Edge computing is a decentralized, distributed network that reduces bandwidth, minimizes latency, and enhances security.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Here are some of the primary benefits of edge computing:
- Reduced latency: Since data is processed close to the source, real-time responses are faster. This minimizes the latency.
- Bandwidth optimization: Data is processed where it is located, and hence there is no need to send vast amounts of data to centralized servers. Thus, the bandwidth usage is reduced.
- Enhanced reliability: There is no need for constant cloud connectivity as systems can function independently.
- Improved data security: Information is not exposed to external threats as it is processed locally, and data travels shorter distances. Because of this, not only is the data transfer faster, but data, especially sensitive data, is protected from risks and breaches.
- Enhanced performance: Networks using edge computing have superior performance and faster response times. There are also fewer periods of downtime.
- Superior insights: Edge computing supports real-time data analytics, hence the quality of corporate decision-making is improved and good insights are available.
- Increased efficiency: Edge devices used in data processing considerably improve the system’s efficiency.
- Improved scalability: Assets can be scaled easily as required because the data is processed on edge where it is located.
- Minimal disruptions: Companies are less reliant on networks with edge computing. With minimal dependency on the network, there are few disruptions.
Edge deployments are a solution to the overcrowded, overloaded centralized enterprise system. In an edge computing system, computing resources are optimized and can be used immediately.
Edge Computing Solutions: Top Use Cases
Edge computing has several impactful applications across industries. These range from autonomous vehicles and remote monitoring to smart grids and in-hospital patient monitoring.
Edge computing specifically enhances applications requiring low latency, real-time analytics, and IoT devices. In this section, we discuss some of the important use cases of edge computing.
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are probably the first and most prominent use cases of edge computing. AVs generates terabytes of data from cameras, LiDARs (Light Detection and Ranging), GPS, and other sensors that should be processed quickly for safety and navigation. AVs are required to make split-second decisions about driving, changing speed, etc. which cloud-based systems cannot achieve as there are latency constraints. To ensure safety and efficiency, real-time decision-making is important for AVs.
How Edge Computing Helps AVs:
- Edge computing enables immediate sensor data analysis to detect obstacles, traffic signals, and pedestrians.
- It reduces dependence on cloud connectivity for critical operations.
- Edge computing supports vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication with minimal latency. It also enables near-instantaneous reaction times that are crucial for avoiding accidents.
2. Edge Computing in IoT: Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Smart Manufacturing
IIoT is the smart factories that use a network of interconnected sensors, actuators, and machines. These systems require fast data processing to optimize operations, monitor equipment, and predict maintenance needs.
How Edge Computing Helps IIoT:
- Edge computing helps with real-time monitoring of machinery to detect anomalies or failures.
- It analyzes sensor data locally and reduces downtime through predictive maintenance.
- Edge computing enhances quality control by processing visual and sensor data on the factory floor.
3. Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring
Edge computing revolutionizes healthcare by enabling real-time data processing in clinical settings and remote care scenarios. Without edge, there might be large amounts of unprocessed data for monitoring devices. These might give rise to security concerns for healthcare providers.
An edge on the hospital site can process the data locally to maintain data privacy and also enable real-time notifications to medical practitioners of unusual patient trends or behaviors.
Edge Computing Use Cases in Healthcare:
- Wearables and medical devices can monitor vitals (heart rate, glucose levels, etc.) and send alerts to patients or doctors in real-time.
- In-hospital edge servers can manage imaging systems (MRI, CT scans) for faster diagnosis.
- Edge aids doctors with timely decision support, thus reducing latency for AI-driven diagnostic tools.
- Patients can be monitored remotely using edge computing, even outside the hospital.
4. Smart Cities
Urban environments are becoming smarter by integrating IoT sensors in traffic lights, surveillance cameras, waste management systems, etc. These smart cities are dependent on huge amounts of data that is also time-sensitive. Using edge computing in smart cities empowers municipalities to make real-time decisions that ensure safety, efficiency, and public satisfaction.
Applications of Edge Computing in Smart Cities:
- Edge-enabled cameras and sensors can reduce congestion in a real-time traffic management system.
- Environmental factors such as air quality and noise levels can be monitored and processed locally for immediate response.
- Edge can help intelligent lighting systems that adapt to human presence (hand gestures) and ambient light conditions.
- Public safety systems that use edge-enabled behavior analysis and facial recognition.
5. Retail and Customer Experience Enhancement
Retail businesses produce a huge chunk of data from sales details, inventory IDs, surveillance footage, and other business details. Edge computing is used to channel this data into appropriate direction by personalizing customers’ shopping experiences, predicting sales and customer preferences, chalking out new campaigns and details for specialized offers, and optimizing vendor orders. Edge computing can also allow retailers to improve operational efficiency and customer experiences by processing data from point-of-sale (POS) systems, sensors, and cameras.
Key Edge Use Cases in Retail:
- Smart shelves that monitor inventory and provide real-time notifications to staff.
- In-store video analytics to analyze customer behavior and optimize store layout.
- Personalized promotions and advertisements take into account proximity and customer profiles.
- Using edge devices with AI-based facial or object recognition to reduce checkout times.
6. Content Delivery and Media Streaming
Content delivery is greatly improved by caching content like music, video stream, web pages, at the edge. With this latency is also reduced significantly. Content delivery networks (CDNs) are also adopting edge computing to meet rising demands for high-quality video content and real-time video gaming.
How Edge Computing Helps in Content Delivery and Media Streaming:
- Edge nodes can be used to cache popular content to reduce latency and improve streaming quality.
- Using edge computing, data that is closer to viewers is processed with minimal delay in live event streaming.
- Cloud gaming platforms use edge data centers to reduce lag and improve responsiveness.
7. Telecommunications and 5G Networks
With advent of 5G networks, operators are finding it difficult to shift to 5G and meet 5G demands for high-speed data transfer, massive IoT connectivity, and low latency of applications such as autonomous driving and augmented reality. Edge computing has proved to be central to the probability and functionality of 5G networks.
Edge computing provides a more flexible and cost-efficient way of deploying 5G networks. Telecom providers are integrating Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) to bring services closer to users. With 5G and edge computing, a new era of connectivity and innovation is being ushered in.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing in 5G Network:
- Edge supports ultra-low latency applications like AR/VR and autonomous driving.
- It enhances 5G network performance by processing data locally.
- Edge computing enables localized services (e.g., regional content delivery, smart stadiums, and events).
- With edge, the cost of deploying and managing network infrastructure is significantly reduced.
- Edge computing allows for easier scaling of network capabilities as demand grows.
- The edge supports a wide range of 5G applications, from IoT to augmented reality (AR).
8. Financial Services and Banking
Banks hold vast amounts of personal data that need high bandwidth capacity and storage space for safekeeping information. Instead of storing and processing data on a centralized server, with edge data processing can be moved close to banks to generate faster and secure banking experience for customers. Edge can also help banks analyze ATM video feeds in real-time to guarantee added safety.
Use Cases in Finance:
- Edge computing can help banks and fintech with real-time fraud detection at ATMs or POS terminals by analyzing transaction patterns locally.
- Smart branches equipped with edge-enabled kiosks offer faster services.
- Edge used in high-frequency trading platforms reduces latency.
9. Predictive Maintenance
Edge computing brings data storage and processing closer to devices or equipment. With this technology, IoT sensors can monitor machine health with low latencies and also perform analytics in real time. Manufacturers using edge computing can analyze and predict potential changes in their production lines before a failure occurs.
Use Cases for Predictive Analytics using Edge Computing:
- Edge computing can analyze data from sensors to predict failures earlier.
- Edge computing allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
- Equipment and production lines are monitored in manufacturing to ensure safety and predict problems before they fail.
10. Cloud Gaming
Cloud gaming is a new type of gaming in which a live feed of the game is streamed directly to devices. The game is processed and hosted in data centers and is highly dependent on latency.
Gaming companies are building edge servers as close to gamers as possible to reduce latency and provide a fully responsive and immersive gaming experience.
How Edge Computing Enhances Cloud Gaming:
- Edge computing provides a more responsive and immersive cloud gaming experience by processing tasks closer to the device, minimizing latency.
- Processing tasks are offloaded to edge nodes. This way, cloud gaming maintains high-quality graphics and seamless gameplay on low-powered devices.
- With Edge, cloud gaming platforms can scale their infrastructure more efficiently and handle larger user bases and peak loads without affecting performance.
- Using edge reduces the need for extensive bandwidth and centralized processing, thus leading to cost savings for cloud gaming providers.
Challenges in Edge Computing Implementation
Despite its benefits, deploying edge computing comes with several challenges:
- Security and privacy: As endpoints increase, there is a larger attack surface endangering security and privacy.
- Management complexity: Coordinating a decentralized network of edge devices is complex, as it requires robust orchestration tools.
- Scalability: As applications scale, edge infrastructure also has to grow, and scaling becomes challenging.
- Interoperability: It may be challenging to integrate devices from different manufacturers without common standards.
Businesses are required to invest in standardized platforms, skilled workforce training, and strong cybersecurity.
Future Trends in Edge Computing
With advancements in AI, IoT, and 5G technologies, edge computing is used extensively. The integration of edge AI is a significant trend today, as AI algorithms run directly on edge devices. Edge AI enables faster processing and more intelligent decision-making at the edge.
Soon, expect to see:
- Hybrid models allow greater convergence of edge and cloud systems.
- Extension of edge applications into education, public safety, and entertainment fields.
- Wider adoption of open-source edge platforms.
- Increased investment in edge computing from major tech players and startups alike.
Conclusion
Edge computing has become very popular in recent years as it has redefined the way data is processed, analyzed, and acted upon across various domains. Edge computing use cases are diverse and impactful, ranging from autonomous vehicles and smart cities to improving patient care and content delivery.
As more organizations adopt digital transformation, edge computing will be a critical enabler of agility, efficiency, and innovation.
By understanding edge computing use cases and preparing for the challenges, businesses can utilize the full potential of edge computing and remain at the forefront of the connected world.
|
|
