What Are the Different Types of Web Developers?
Consider your most regularly used apps, like Netflix for binge watching, Instagram for doom scrolling, or Uber Eats for ordering food. It seems second nature to us. Different types of developers collaborate behind the scenes, including front-end developers who build what you see, back-end developers who power what you don’t, full-stack developers who bridge the two, and experts in CMS, security, and mobile.
In the early days of the internet, one single person could build a whole website by themselves. These days, development is much more specialized as organizations execute secure banking apps or massive e-commerce platforms. Understanding the different types of web developers helps organizations in hiring in a more efficient manner and helps potential developers in making the best decision.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
Why Understanding the Types of Web Developers Matters
The importance of understanding the differences between web development roles is often ignored by businesses. Without defining the scope, hiring “just a web developer” can lead to mismatched expectations, resource wastage, and significant delays in the project.
For Organizations and Hiring Managers
- Employ the best talent: Align specific skill sets with project requirements.
- Create balanced teams: For holistic coverage, bring together front-end, back-end, and security experts.
- Sensible budgeting: Hire specialized personnel only when required to avoid overspending.
For Aspiring Developers
Understanding these types helps those new to the industry make sense of their career choices. Front-end development may be more interesting to someone who is passionate about visual design. However, back-end development may be more appealing to someone who enjoys solving logical issues and managing data. Full-stack development might be more satisfying for developers who value adaptability.
For Project Success
- Front-end developers ensure that the product is user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing.
- Scalability and security are ensured by back-end developers.
- Niche requirements such as accessibility compliance, mobile-first optimization, and e-commerce checkout flows are handled by skilled and specialized developers.
To summarize it, understanding the different types of web developers is not only theoretical, but it is also a practical requirement for digital projects to be successful.
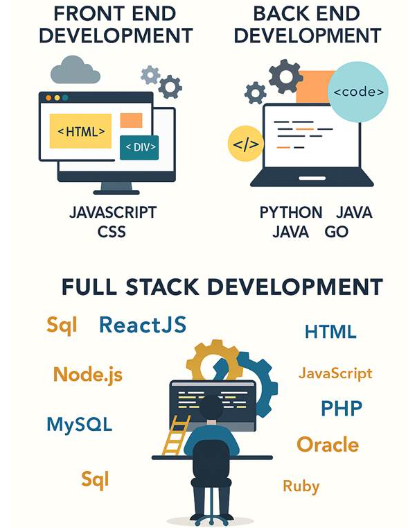
The art of building everything that users see and interact with on an application or website is called front-end development. It builds user experiences that are intuitive, responsive, and engaging by integrating design principles with coding.
Key Responsibilities of Front-End Developers
- Making design a reality: Front-end developers leverage HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to develop wireframes and mockups built by UI/UX designers.
- Ensuring responsiveness: A modern website needs to function and appear consistently the same across smartphones, tablets, and PCs. To do this, developers use frameworks like Tailwind or Bootstrap, media queries, and flexible layouts.
- Performance optimization: Front-end developers work to reduce JavaScript/CSS bundles, utilize lazy loading, and compress images in order to accelerate page loads.
- Accessibility compliance: They guarantee that websites comply with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which permits keyboard navigation and screen reader compatibility.
Popularly Used Tools and Frameworks in Front-End Development
- Languages: JavaScript (functionality), CSS3 (style), and HTML5 (structure).
- Frameworks and libraries: Vue.js (lightweight interactivity), Angular (enterprise apps), and React (component-based UI).
- Version control: Git/GitHub for teamwork.
- Build tools: Webpack, Babel, and task runners like Grunt or Gulp.
Real-World Example of Front-End Development
Imagine a website for booking travel. Front-end functionalities like the search bar, filters, interactive calendar, and map results need to be fast, simple, and responsive to mobile devices. Even the strongest back end would be useless to end-users without front-end developers.
Back-End Developers: Powering the Server-Side Logic
The back-end logic is everything users depend on but cannot see, whereas the front-end is what they see. Back-end developers build the website’s “plumbing,” making sure that features work, transactions are safe, and data flows seamlessly.
Key Responsibilities of Back-End Developers
- Database management: Building queries, designing schemas, and making sure that data is stored and retrieved efficiently.
- Server-side logic: Writing the application code that handles user requests, validates user identity, and generates responses.
- API development and integration: Building GraphQL or RESTful APIs to link mobile apps, front ends, and external services.
- Service enforcement: Defending against attacks (SQL injection, XSS, CSRF), managing authentication (OAuth, JWT), and encrypting sensitive data.
- Performance and scalability: Writing code that supports thousands or millions of users simultaneously without facing any issues.
Language and Frameworks in Back-End Development
- Languages: Node.js (Express.js), Ruby (Ruby on Rails), PHP (Laravel, Symfony), Python (Django, Flask), and Java (enterprise systems).
- Databases: NoSQL (MongoDB, Redis) and Relational (MySQL, PostgreSQL).
- Cloud and Servers: Azure, Docker, GCP, AWS, and Kubernetes for scaling and deployment.
Real-world example of Back-End Development
- The product is displayed and added to the cart via the front end.
- The back end sends a confirmation email, updates the order database, processes payment via an API (like Stripe or PayPal), and validates inventory.
Full-Stack Developers: Connecting Front-End and Back-End
The best features of both worlds are merged by full-stack developers. They are perfect for small teams and rapid prototyping because they feel at ease working on both the user-facing side and server-side logic.
Key Responsibilities of Full-Stack Developers
- Building and maintaining applications’ front-end and back-end.
- Managing databases, developing APIs, and writing client-side logic.
- Deploying apps to servers or the cloud.
- Solve issues with the complete technology stack.
Popular Tech Stacks for Full-Stack Development
- MERN: MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js
- MEAN: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js
- LAMP: Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP
- Django + React/Vue: Python-based back end with modern JS front end
Why Businesses Value Full-Stack Developers
- Efficiency: Reduces the time it takes for front-end and back-end experts to hand off.
- Versatility: Able to fill either position based on the requirements of the team.
- Economical: Ideal for new businesses with tight budgets.
Real-World Example of Full-Stack Development
Without the need for additional experts, a startup’s full-stack developer can build the user interface for a website, configure the server, link it to a database, and launch the application on AWS.
Mobile and Hybrid Web Developers
Developers with expertise in mobile-first and hybrid applications are now vital since mobile users have outnumbered desktop users. These developers ensure that apps and websites run seamlessly on all platforms.
Key Responsibilities of Mobile Developers
- Building Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that combine the best features of the web and mobile (push notifications, offline functionality, home-screen installation).
- Developing hybrid applications utilizing frameworks like Flutter, Xamarin, or React Native.
- Enhancing mobile performance through methods such as image compression, code splitting, and caching.
Tools and Frameworks Used by Mobile Developers
- Flutter: Google’s framework for building native-like apps with a single codebase.
- React Native: JavaScript cross-platform apps.
- PWAs: Web app manifests, caching techniques, and service workers.
Real-World Example of Mobile Development
Think of PWAs that simulate native mobile apps, work offline, and load faster, such as Instagram or Twitter Lite. These types of experiences are built by mobile developers to serve emerging markets or users with restricted bandwidth.
CMS and e-Commerce Developers
Not all websites need a total coding overhaul. To accelerate development, many depend on e-commerce frameworks and CMS platforms. Their systems’ developers prioritize customization and scalability.
CMS Developers
- Use cases: Blogs, corporate websites, and news portals.
- Platforms: WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla
- Responsibilities: Custom themes, plugins, database integration, content migration, and SEO optimization.
E-commerce Developers
- Use cases: Online stores, subscription-based companies, and marketplaces.
- Platforms: Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce.
- Responsibilities: Security implementation, payment gateway integration, third-party integrations (ERP, CRM), and product catalog management.
Real-world Example of CMS and e-Commerce Development
While a Shopify developer would focus on developing a fast, safe online store with integrated payment systems, a WordPress developer might utilize custom plugins to develop a business blog.
Web Security and Performance Developers
As performance needs and cyber threats increase, some developers concentrate on building dependable, secure, and fast websites.
Responsibilities
- Security: Setting up intrusion detection systems, firewalls, encryption, and secure authentication.
- Performance optimization: Using CDNs, caching (Redis, Varnish), decreasing HTTP requests, and database optimization.
- Compliance: Ensuring that websites adhere to industry-specific guidelines, such as the CCPA, GDPR, or HIPAA.
Tools and Best Practices
- Security tools: OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, and SSL/TLS certificates.
- Performance tools: Google Lighthouse, Pingdom, and GTMetrix.
Real-World Example
In order to satisfy user expectations, developers of healthcare platforms must ensure HIPAA compliance, encrypt patient data, and make sure the application loads in less than a second.
Emerging Specializations in Web Development
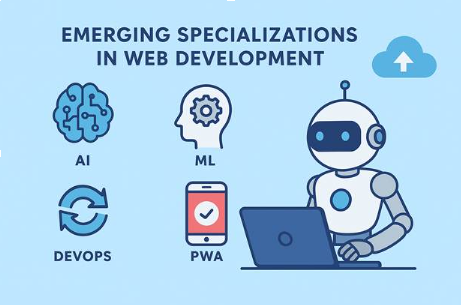
Web development is an industry that is always evolving. These days, cloud AI and user experience trends have guided developers to specialize in new fields.
DevOps and WebOps Developers
Utilize cloud infrastructure, Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD pipelines to focus on deployment, monitoring, and scaling.
Web Accessibility Experts
Make sure websites are usable by individuals with disabilities by complying with WCAG accessibility guidelines. This entails keyboard navigation support, color contrast testing, ARIA roles, and semantic HTML.
Progressive Web Apps Developers
Blend the best features of the web and mobile platforms to produce fast, installable, and offline-capable apps. Organizations like Starbucks, Pinterest, and Twitter are leveraging PWAs more and more.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Developers are integrating AI-powered personalization tools, recommendation engines, and chatbots into modern web applications.
Real-World Example
While a PWA developer might create a travel booking app that works offline and syncs when the user reconnects to the internet, a DevOps developer might utilize Kubernetes to automate deployment to AWA with zero downtime.
Why Testing Matters
- Validates business processes like payments, signups, and logins.
- Eliminates expensive bugs and downtime.
- Secures against security flaws.
- Ensures cross-browser and cross-device compatibility.
Testing Types Relevant to Web Developers
- UI/UX testing: Validates that the interface is responsive, user-friendly, and accessible.
- Integration testing: Validates that databases, APIs, and front-end components interact correctly.
- Unit testing: Ensures that individual code components work as intended.
- Performance testing: It assesses a site’s speed, load-handling capacity, and scalability.
- Security testing: It detects vulnerabilities and validates regulatory compliance.
Selecting the Right Type of Web Developer
- Basic websites: Front-end + CMS developers.
- Dynamic web apps: Full-stack developers.
- Data-heavy applications: Front-end assistance + back-end development.
- Mobile-first apps: Mobile web developer
- E-commerce platforms: Security developer and e-commerce expert.
While startups often prefer employing flexible full-stack developers, larger teams often combine multiple roles.
Examples of Best-Fit Scenarios
- Local business website: Content creation and management by a front-end developer and CMS specialist.
- Enterprise Software as a Service (SaaS): A group of developers comprising front-end, back-end, full-stack, and DevOps who collaborate.
- E-commerce startup: Back-end API expert and e-commerce developer to manage payments, orders, and security.
- Mobile-first product: A hybrid/ mobile developer using React Native or Flutter to develop cross-platform applications.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
A common mistake made by organizations is to believe that a single developer can “do it all.” For very small projects, that might work, but experts are required for complicated applications. Time-to-market is reduced, scalability is improved, and technical debt is prevented by choosing the right mix.
Conclusion
With multiple specialized roles, web development has developed into a successful ecosystem. Today’s digital experiences are highly influenced by a wide range of professionals, including front-end and back-end developers, CMS specialists, security experts, and full-stack engineers.
Testing becomes just as important as coding as applications get more complicated. Web developers can deliver excellent solutions faster with tools, ensuring that their applications and websites satisfy user needs while maintaining dependability and security.
Comprehending these different roles and the tools that support them will help you achieve success in today’s fast-paced digital landscape, whether you are a developer planning your career path or an organization trying to hire the most relevant expertise.
Additional Resources
- Web Development Technologies: A Complete Guide
- Top 10 Backend Technologies Every Developer Should Know
- Which Version Control System is the Best?
- Top 10 Natural Language Processing Tools
|
|
