What is AutoML? Automated Machine Learning Explained for Developers
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have evolved from niche research fields into essential technologies as they drive innovation across industries, from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and marketing. However, developing high-performing ML models requires deep expertise, extensive experimentation, and significant time investment.
This growing complexity of ML models and an increasing demand for rapid deployment have inspired the rise of Automated Machine Learning (AutoML).
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
This blog on AutoML will explore the concept of AutoML, its components, how it works, its benefits, challenges, and applications.
AutoML in AI Development – Definition, History, & Core Components
AutoML is the process of automating the complex, iterative, and time-consuming tasks in the end-to-end lifecycle of machine learning model development. The tasks include data preprocessing, feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning, model evaluation, and even deployment.
AutoML aims to: make machine learning accessible, efficient, and scalable.
When repetitive and time-consuming tasks are automated, data scientists can focus more on interpretation and strategy instead of managing tedious experimentation.
AutoML streamlines AI workflows for data scientists and developers, while also enabling non-experts to create and implement AI systems.
Without AutoML to automate tasks, every step in the ML workflow, like data preparation, data preprocessing, feature engineering, and hyperparameter optimization, must be carried out manually. This process is too lengthy and tedious.
AutoML tools simplify the process of building ML models and facilitate AI implementation in regulated industries with their reproducible and explainable results.
Users benefit from an intuitive interface as they can use it to create, train, validate, and deploy generative AI models and other deep learning systems.
- Cleaning the data
- Choosing the right model
- Tuning the model settings (called hyperparameters)
- Testing and improving the model
But with AutoML, most of these steps are automated using smart tools, making the ML process faster, easier, and more accessible to non-experts.
A Brief History
- The concept of AutoML emerged in the late 2000s as researchers began exploring ways to simplify ML workflows.
- Initially, ML requires highly specialized expertise in statistics, algorithms, and programming.
- As datasets grew larger and more complex, there was an urgent need for automation.
- In the 2010s, academic projects, including Auto-sklearn, TPOT, and Auto-WEKA, introduced the first open-source frameworks capable of automatically optimizing ML pipelines.
- Soon after, tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon came up with commercial AutoML platforms such as Azure AutoML, Google Cloud AutoML, and Amazon SageMaker Autopilot, making them available for a wider audience.
The Core Components of AutoML
It is essential to look at the core processes that AutoML automates to understand how it works. These components are identical to the steps a data scientist takes when manually building a model.
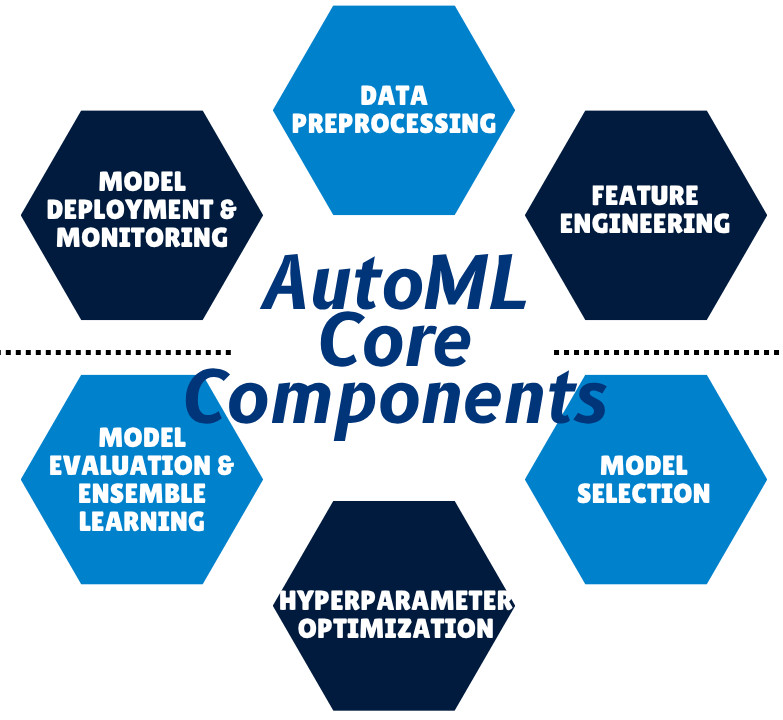
1. Data Preprocessing
AutoML starts by cleaning the raw data with steps like dealing with missing values, removing duplicates, and handling outliers. Data transformation, such as normalization, is also performed by AutoML. Other transformation tasks, like encoding categorical variables or scaling numeric features to make them compatible with algorithms, are also undertaken by AutoML.
Some advanced AutoML systems even detect data imbalance or perform automated feature selection that improves performance and prevents overfitting.
2. Feature Engineering
- Feature Generation: Creating polynomial, interaction, or aggregate features.
- Feature Selection: Identifying the most informative features and removing redundant ones.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Simplifying models using techniques such as PCA (Principal Component Analysis).
In modern AutoML systems, feature extraction by analyzing data can be performed by deep learning architectures that learn features directly from raw inputs, such as images or text.
3. Model Selection
AutoML platforms automate model selection or choosing the correct algorithm by evaluating multiple algorithms, such as decision trees, random forests, gradient boosting machines, and neural networks, and selecting the best-performing model for the given data and problem type (classification, regression, clustering, etc.).
4. Hyperparameter Optimization
Hyperparameters are the parameters that influence the performance of the ML model. Most ML models have hyperparameters like learning rate, tree depth, or number of layers that need to be tuned for optimal performance.
- Grid search
- Random search
- Bayesian optimization
- Evolutionary algorithms
This hyperparameter optimization to find the best hyperparameter configuration is one of the most computationally intensive yet impactful parts of AutoML.
5. Model Evaluation and Ensemble Learning
AutoML frameworks automatically evaluate models using metrics and cross-validation appropriate for the task (e.g., accuracy, F1-score, RMSE). They can also combine multiple high-performing models into ensembles that enhance overall predictive accuracy through approaches such as bagging, boosting, or stacking.
6. Model Deployment and Monitoring
Modern AutoML tools streamline deployment and monitoring in addition to model creation. Users can deploy models as APIs, integrate them with production systems, and set up monitoring pipelines to detect performance degradation or drifts with just one click.
How AutoML Works
AutoML uses sophisticated algorithms to automate each stage of the traditional ML process. The entire process can be completed in hours or even minutes, rather than days or weeks, when done manually. AutoML solutions construct numerous ML pipelines to handle the intended task, then identify the optimal choice.
Model evaluation and selection are integral to an iterative process that selects the most suitable model for the task. Data visualization tools are used to bring more ease of use.
Every stage of the ML pipeline is automated by AutoML, resulting in greater efficiency and better results compared to traditional pipelines, which are time-consuming, resource-intensive, and prone to human error.
The ML pipeline consists of the following steps:
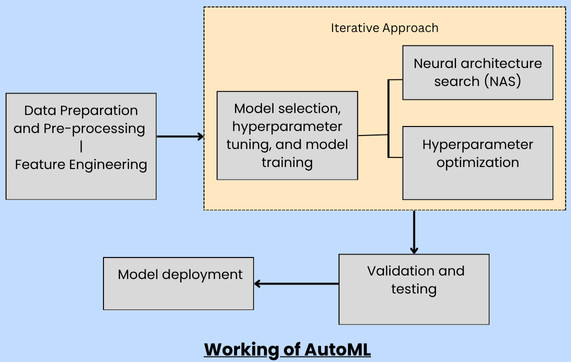
1. Data Preparation and Pre-processing
The data preparation process collects the raw data and integrates it into a training dataset. This step helps to ensure that training data is free from bias and sets up a model for success, as accurate data leads to accurate predictions and insights.
The data preparation phase takes place before an AutoML solution is deployed. The AutoML solution further preprocesses and cleans the data, which leads to a better AI model performance. AutoML handles feature engineering on behalf of users to select the data features that are most suitable for improving model performance.
Feature Engineering
This is a transformative process by which a data scientist draws new information from input data and prepares it for machine learning. Dataset attributes called data features or variables are used to make predictions and decisions.
- Exploring the feature space
- Filling missing values
- Selecting features to use
2. Model Selection, Hyperparameter Tuning, and Model Training
AutoML tools automatically build and train several models simultaneously with a range of algorithms and hyperparameter configurations. This is unlike traditional ML, which requires expert knowledge of AI model types in addition to their respective capabilities and limitations.
Many AutoML solutions combine several models in ensemble learning.
Neural Architecture Search (NAS)
NAS automates the creation of neural architecture and multi-layered networks with complex hyperparameter configurations. These are required by advanced tasks. Automating this process reduces the time spent and potential for error. Using advanced algorithms, NAS identifies the optimal architecture based on the dataset and context.
Hyperparameter Optimization
Hyperparameters govern the model’s learning process and are external to the model. They are configured by data scientists. The neural network structure of the model is defined by hyperparameters.
With automated hyperparameter optimization, teams can iterate and experiment to discover the best hyperparameters across features and models. AutoML also automates hyperparameter tuning through advanced algorithms such as Bayesian optimization. It frees data scientists to focus on the why of model creation rather than how.
3. Validation and Testing
ML algorithm’s progress during training is validated by data scientists. Once training is over, the model is tested with new data to evaluate the performance before real-world deployment using metrics including a confusion matrix, F1 score, ROC curve, and others.
Once training is completed, AutoML tools test each model to identify the model that performs best on the training and test datasets. It then automatically selects the top-performing model for deployment.
4. Model Deployment
In this phase, completed models are made available to users, monitored for performance, and maintained over time to ensure reliability and accuracy. Without automation, this step would require scripts and systems to integrate the model into their operations and deliver it to users.
Many AutoML tools include deployment tools for seamless real-world integration. Models can also be deployed as a service accessed through a website, API connection, or an app.
Popular AutoML Tools and Frameworks
Several open-source and commercial AutoML platforms are available today, each with its unique strengths. Here, we have listed some of these platforms:
Open-Source Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto-sklearn |
|
| TPOT (Tree-Based Pipeline Optimization Tool) |
|
| H2O AutoML |
|
| AutoGluon |
|
| PyCaret |
|
| AutoKeras |
|
| MLBox |
|
Commercial Platforms
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Google Cloud AutoML | Simplifies model training for vision, translation, and structured data. |
| Microsoft Azure AutoML | Provides automated ML pipelines integrated with Azure’s data ecosystem. |
| Amazon SageMaker Autopilot | Automates model creation and deployment on AWS infrastructure. |
| DataRobot | A powerful enterprise AI platform that automates the entire process of building, deploying, and maintaining machine learning models. |
| Dataiku | A comprehensive AutoML platform designed to streamline end-to-end machine learning workflows. |
| H2O.ai | Offers commercial AutoML capabilities focused on model selection and training, built upon the open-source H2O platform. |
All these tools typically share the core principle of automating ML tasks, but differ in terms of scalability, usability, interpretability, and integration with enterprise workflows.
Benefits of AutoML
- Easy for Beginners: AutoML does not require a machine learning expert; even non-experts can utilize it.
- Democratization of AI: It makes ML accessible to non-experts, as business analysts, product managers, and domain specialists can build ML models without needing to code or understand complex algorithms.
- Efficiency and Speed: AutoML significantly reduces the time required to create a model, from weeks or months to hours. Automating trial-and-error experiments helps the team to deploy solutions faster and iterate rapidly.
AutoML automates many complex tasks, saving hours or even days of manual work.
- Improved Model Performance: AutoML systematically explores a wide range of algorithms and hyperparameters, often discovering models that outperform manually designed ones, especially in large or complex datasets.
- Cost Reduction: Organizations save on data science labor costs and computational resources as fewer steps are required to build the model. AutoML also minimizes human error in preprocessing or tuning.
- Scalability: AutoML systems are well-suited for handling large-scale model generation, particularly when multiple predictive models are required for different departments, markets, or customer segments.
- Integration and Deployment: Modern AutoML tools integrate seamlessly with data pipelines and cloud platforms, resulting in smoother deployment and more manageable maintenance.
- Helps Businesses: Companies can utilize AutoML to analyze data and make informed predictions, such as understanding customer behavior, forecasting sales, or detecting fraud, without hiring a large ML team.
Challenges of AutoML
- Loss of Transparency: AutoML-generated models can result in “black-box” models that are difficult to interpret and understand. Ensuring fairness, explainability, and compliance can be challenging, particularly in regulated industries such as healthcare and finance, without a thorough understanding of the model’s workings.
- Data Quality Dependence: Any AI model is as strong as its data. It cannot fix poor-quality data. Models can amplify biases if the data is not reliable. This overdependence of models on data quality might be a drawback.
- Limited Customization: AutoML effectively covers most general cases, but may still fall short of matching the performance of a custom-designed solution developed by experienced data scientists for specialized tasks or architectures.
- Computational Cost: AutoML encompasses extensive functionality and hyperparameter searches, which are computationally expensive. Some processes require robust infrastructure, such as those for deep learning tasks. This way, AutoML costs can quickly spiral out of control if the technique is applied to creating complex models.
- Overfitting and Bias: If not carefully configured, AutoML models may overfit the data, and automated feature selection can unintentionally propagate societal or data biases.
Applications of AutoML
AutoML is being utilized across sectors to drive smarter, faster decision-making. Some of the applications of AutoML are:
1. Healthcare
Predictive models for disease detection, patient risk scoring, and drug discovery can be developed using AutoML. Even when clinical expertise is limited, AutoML can be utilized to predict patient readmissions using historical data.
2. Finance
Banks use AutoML for credit scoring, fraud detection, and algorithmic trading. Automation enables rapid model updates as new data streams in, improving adaptability to market changes.
3. Retail and E-commerce
Retailers utilize AutoML to forecast demand, recommend products, and dynamically optimize pricing. AutoML models can predict customer churn and personalize promotions by analyzing transaction data.
4. Manufacturing
Industries use predictive maintenance to anticipate equipment failures by analyzing sensor data. Utilizing AutoML can reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
5. Marketing
Campaign optimization, customer segmentation, and lead scoring can be done using AutoML. Marketers can run sophisticated predictive analytics without deep ML expertise.
6. Natural Language and Vision
AutoML frameworks, such as Google Cloud AutoML Vision and Translation, enable organizations to build models for text classification, image recognition, and sentiment analysis, even without a large ML team.
AutoML vs. Manual ML
Having got a basic understanding of AutoML, here are the key differences between AutoML and traditional machine learning:
| Aspect | AutoML | Traditional/Manual ML |
|---|---|---|
| Expertise Required | Low or no expertise, as even non-experts can develop models. | High expertise required with data science knowledge. |
| Development Time | Takes hours to days to develop a model. | Takes a long time sometimes, from weeks to months. |
| Flexibility | Not very flexible, limited by tool capabilities. | Fully customizable. |
| Transparency | Maybe opaque. | Complete control and understanding. |
| Scalability | Automated scaling. | Manual scaling. |
| Performance | Often optimized automatically. | Dependent on expertise. |
In essence, AutoML complements data scientists rather than replacing them. It automates routine tasks, freeing up experts’ time for them to focus on complex and strategic tasks, such as feature design, interpretability, and domain insights.
The Future of AutoML
- Neural Architecture Search (NAS): AutoML is increasingly being used in deep learning through NAS to design optimal neural network architectures. This has led to breakthroughs in computer vision and natural language processing (NLP).
- Explainable AutoML: The next generation of AutoML tools integrates frameworks that help users understand model decisions and maintain transparency, emphasizing interpretability and explainability.
- AutoML for Edge Devices: With the rise of IoT and mobile devices, lightweight AutoML models are being developed to run efficiently on edge devices, enabling real-time intelligence without cloud dependency.
- Integration with MLOps: AutoML, when integrated with MLOps, enables continuous model training, deployment, and monitoring pipelines with minimal human intervention.
- Generative AutoML: Generative AI techniques are being increasingly utilized by industries, and in the near future, they may be used to dynamically create optimized ML pipelines, code, and features, further reducing human effort.
Conclusion
AutoML is, without doubt, a revolutionary step in the evolution of AI. Automating the complex, repetitive parts of ML enables faster innovation, reduces obstacles to entry, and scales AI capabilities across sectors.
However, in achieving this, there should be a balance; automation should assist, not replace, human expertise. Data scientists and domain experts must collaborate to ensure ethical integrity and inform strategic applications.
In the future, AutoML will continue to evolve into a central pillar of AI development, making intelligent systems more interpretable, accessible, and impactful than ever before.
|
|
