What is Mobile Application Development?
Just imagine being able to work with a system like Tony Stark’s J.A.R.V.I.S! The ability to communicate with it, receive real-time updates, and immediately deploy commands. Yes, while this is fiction, it is not too different from the real-world mobile apps we interact with on a daily basis. Ride-sharing platforms, smart home systems, banking apps, and fitness trackers are all examples of this, and they operate at an advanced level of intelligence and responsiveness.
Mobile is the present, not the future- a quote you would be aware of. It is a common fact that apps on mobile devices are used for more than 90% of the time. These apps have changed the very fabric of our communication, shopping, travel, banking, and even dating habits.
Mobile app development is at the core of modern innovation, right from an entrepreneur building the next big thing to a major enterprise optimizing its internal processes.
This blog takes you through the entire journey of mobile application development, right from understanding what is the process, designing, and testing the product with testing tools.
What Is Mobile Application Development?
At its core, mobile app development is the practice of developing software for mobile devices, like smartphones, wearable technology such as smartwatches, or tablets. But it’s more than just writing code; it entails developing quick, easy-to-use, safe, and scalable experiences. These apps can be delivered as web applications with server-side or client-side processing, or they can be pre-installed during manufacturing.
Consider how Instagram was started as an iOS photo-sharing app. Due to the continuous mobile development and innovation, it has evolved into a globally used platform with integrated video, messaging, e-commerce, and AI recommendations.
- Research and Idea: Determining market gaps, understanding user needs, and defining essential app features.
- Design and prototyping: Creating user-experience (UX) focused interfaces that are both visually pleasing and intuitive.
- Frontend and Backend Development: Building the server-side (data storage, authentication, etc.) and client-side (what users interact with) logic.
- Quality Assurance (QA): Ensure that the applications run consistently on different hardware and operating systems.
- Launch and Deployment: Apps are published on online stores like Google Play and Apple App Store.
- Continuous Maintenance: Feature enhancements, regular updates, and performance optimization.
Relying on the platform and type of app, developers use a wide range of languages, tools, and frameworks. Android and iOS are the two most favored mobile operating systems.
Types of Mobile Applications: Native, Hybrid, and Web Apps
Stakeholders and developers can choose the best development path for their goals, budget, and schedule by having a deep comprehension of the different types of mobile applications.
Native App Development
- Android: Java or Kotlin.
- iOS: Swift or Objective-C.
- Improved performance as a result of direct hardware interaction.
- Access to all device APIs and functionalities, such as camera, push notifications, and GPS.
- Better user experience as a result of platform-utilized UI/UX.
- Needs distinct development for each platform (i.e., two codebases)
- It results in higher development costs and a longer timeline.
Native apps are ideal for apps that demand high performance, innovative user interface interactions, or integration with device-specific features such as AR/VR or gaming apps.
Hybrid Apps Development
Web technologies (JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS) are employed for the development of hybrid applications, which are then deployed within native containers. Ionic, PhoneGap, and Cordova are prominent frameworks.
- A single codebase for multiple platforms.
- Faster deployment and development.
- Economical.
- Slower performance compared to the native apps.
- Limited availability of certain device-specific features.
- UI might not feel fully “native” to the users.
Hybrid apps are the ideal option for MVPs and startups with constrained funds and time to market.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
These are technically websites that are optimized for mobile devices and work similarly to native apps. They can send push notifications, work offline, and be added to the home screen.
- Platform-agnostic.
- Easy to update.
- Does not need app store deployment.
- Not relevant for apps requiring intensive hardware integration.
- Restricted functionality in comparison to native apps.
PWAs are ideal for content-driven apps or services where eliminating installation hurdles is vital.
The Mobile App Development Process
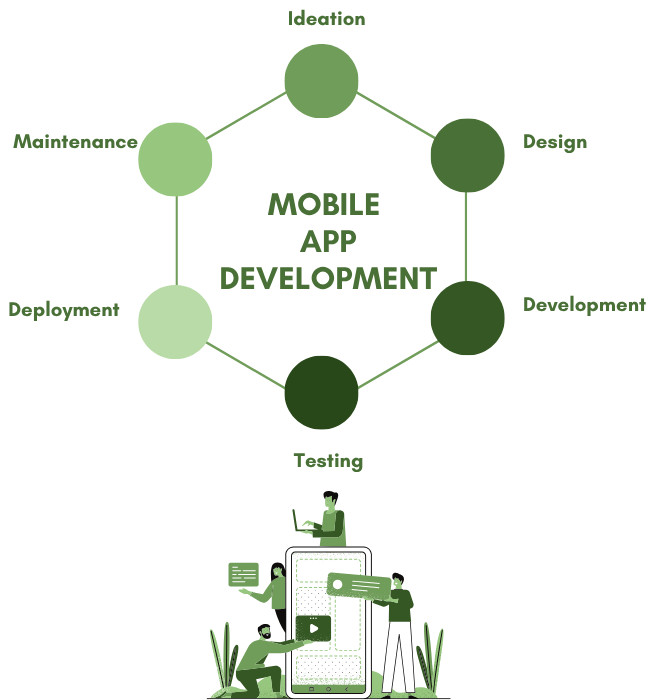
On-time delivery and quality control are ensured by a structured mobile app development process. The vital phases are explained below:
Strategy and Planning/ Ideation
- Business objectives.
- User personas and target audiences.
- Competitor analysis.
- Success metrics (KPIs).
- A functionality list and roadmap.
Based on the goals, it also involves deciding whether to employ Android, iOS, or both, as well as whether to opt for hybrid, native, or cross-platform.
UI/UX Design
- Developing interactive prototypes.
- Sketching a wireframe to establish the layout.
- Designing aesthetically pleasing UI components.
- Ensuring device accessibility and responsiveness.
App Development
- Writing code for frontend and backend logic.
- Setting up the development environments (emulators, libraries, IDEs).
- Connecting databases, third-party services, APIs, and cloud backends.
Testing
As discussed further down in this blog, the testing stage ensures the application is dependable, functional, and safe.
Implementation/ Deployment
- Preparing metadata (icons, screenshots, and descriptions).
- Ensure that the App Store and Play Store guidelines are adhered to.
- Handling rollout and post-launch monitoring.
Maintenance and Updates
- Adding new features based on analytics and trends.
- Updating for OS versions.
- Resolving bugs based on user feedback.
What to Choose: Cross-Platform vs. Native App Development?
A range of critical considerations should influence the choice between developing native and cross-platform apps:
- Native apps perform at their optimum as they are platform-specific.
- Cross-platform apps often lag a little in high-performance use cases such as games with loads of graphics, despite using advanced technologies like React Native and Flutter.
- Cross-platform apps enable developers to reuse a single codebase, which can save up to 40% on development time and costs.
- Native development demands separate teams and resources for iOS and Android
- Native apps provide a smoother user experience by strictly adhering to platform-specific UI/UX guidelines.
- Cross-platform apps do aim for a seamless and consistent user experience; however, they may not feel as “natural” across platforms.
- It would demand a lot of resources to maintain just two native apps.
- Yes, cross-platform apps make maintenance simplified, but they may need to sacrifice platform-specific functionality.
In summary, choose cross-platform for rapid deployment and wider reach, and native apps for apps with a lot of features or performance.
The Role of Testing in Mobile Application Development
To ensure that apps satisfy usability, security, and functionality requirements, testing is a critical part of the mobile app development process.
Why is Mobile App Testing Important?
Multiple devices, screen sizes, network configurations, and OS versions are used by mobile apps. Even minor defects can lead to negative reviews, lost revenue, and uninstalls if they are not thoroughly validated.
Mobile App Testing Types
- Functional testing: It validates that every feature functions as expected. Validates that user interactions are working as expected.
- UI/UX testing: Validates that the transitions, layouts, and design of the application are consistent, easy to use, and responsive.
- Performance testing: Examines resource consumption, load times, and app speed in both generic and severe scenarios.
- Security testing: Detects weaknesses like insecure data transmission or storage.
- Compatibility testing: Ensures smooth working across multiple hardware configurations, OS versions (like iOS 16 vs iOS 17), and screen sizes.
- Regression testing: It ensures that the updates or changes to code don’t affect the already successfully running features.
App reliability is boosted, time to market is accelerated, and customer satisfaction is increased when testing is properly integrated into the development lifecycle.
Best Practices for Successful Mobile App Development
-
Define precise goals and KPIs: Establish measurable, unambiguous goals initially.
- Who is the intended audience?
- What issue is solved by the app?
- Which metrics (retention, revenue, and downloads) will be used to calculate success?
-
Select the Right Development Plan: Choose between hybrid, native, or cross-platform based on:
- Budget.
- Timeline.
- Required characteristics.
- Maintainability.
-
Stress Performance and UX: An app that is slow or complicated to use will rapidly lose users. Invest in:
- Load time optimization.
- Responsive UI/UX designs.
- Offline capabilities if required.
-
Implement Scalable and Secure Architecture: Ensure your backend can accommodate user growth. Comply with privacy regulations (such as GDPR), use secure authentication and encryption.
-
Prioritize QA and Testing: Include mobile testing right from day one. Use test automation tools such as:
- Early bug identification.
- Reduced testing time.
- Dependable performance across environments.
-
Gather Feedback and Iterate: Post-launch analytics and user feedback help in feature optimization and prioritize future development.
The Future of Mobile App Development
The field of mobile app development is evolving rapidly. The future is filled with opportunities and challenges for businesses and developers, both fueled by developments in AI-powered technologies, connectivity, and user expectations.
5G Technology will Optimize App Performance
- Real-time collaboration tools like virtual workspaces or design apps.
- AR navigation tools for in-person interaction.
- Real-time streaming gaming applications that run on the cloud (such as Xbox Cloud Gaming).
AI and Machine Learning will Drive Personalization
- Personalize content delivery (Netflix’s AI-driven recommendations).
- Forecast user behavior (Spotify’s Discover Weekly).
- Improve automation (e.g., intelligent scheduling or chatbots).
Even AI-powered writing tools such as Grammarly and habit tracking health are only the tip of the iceberg.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
Apps will behave as central control hubs more and more as smart devices are adopted into workplaces and homes.
- Wearable connected to health and fitness ecosystems (e.g., Apple Watch + iPhone + Healthkit).
- Industrial apps for machinery monitoring in factories.
- Smart home control apps (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Home).
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR)
- Games like Pokémon GO and Call of Duty.
- IKEA Place allows users to visualize furniture in their spaces.
- VR learning platforms offer skill simulations or virtual training.
Low-code and No-code App Development
- Reduces development costs.
- Encourages innovation within organizational teams.
- Accelerate the development of MVPs.
Escalating Need for AI-Powered Testing
- Continuous integration testing.
- Faster, scalable test creation.
- AI-powered adaptability to UI modifications.
Designing Smarter, Better Apps
Mobile apps have transformed the world, whether it is the Strava app that monitors your morning run, a virtual classroom app that guides young minds, or a payment app that helps users access digital banking.
And the best part? We have only just started!
Alan Kay has rightly echoed this emotion with his quote, “The best way to predict the future is to invent it.”
The platforms, tools, and frameworks available to developers today didn’t even exist just five years ago. Building high-quality apps is now faster, simpler, and more collaborative than ever due to upcoming tools and technologies.
Whether you’re coding, managing, or testing a mobile app, adapt innovation, keep the user in mind, and employ automation to build with confidence.
Additional Resources
- What are the Different Types of Code Smells?
- What is Code Optimization?
- Top 10 Natural Language Processing Tools
|
|
