Microservices Interview Questions – Software Engineering
Microservices have been making their presence felt in software development since the term was coined. Microservices, a microservice architecture, is a variant of service-oriented architecture (SOA) for developing large applications where services are granulated into chunks per business domains. It enables the continuous delivery/deployment of complex applications and makes the application easier to understand, develop, and test, and is more resilient to architectural erosion.
The microservice architecture is one of the hottest topics in the software industry because of its ability to provide modularity, availability, and scalability. Many businesses are keen to adopt microservices architecture as the provide a new way to interface in new way to deliver software solutions quickly.
This article gives a brief overview of microservices in software engineering followed by top 30 interview questions and answers, a microservices professional can expect when he/she interviews for the relevant post.
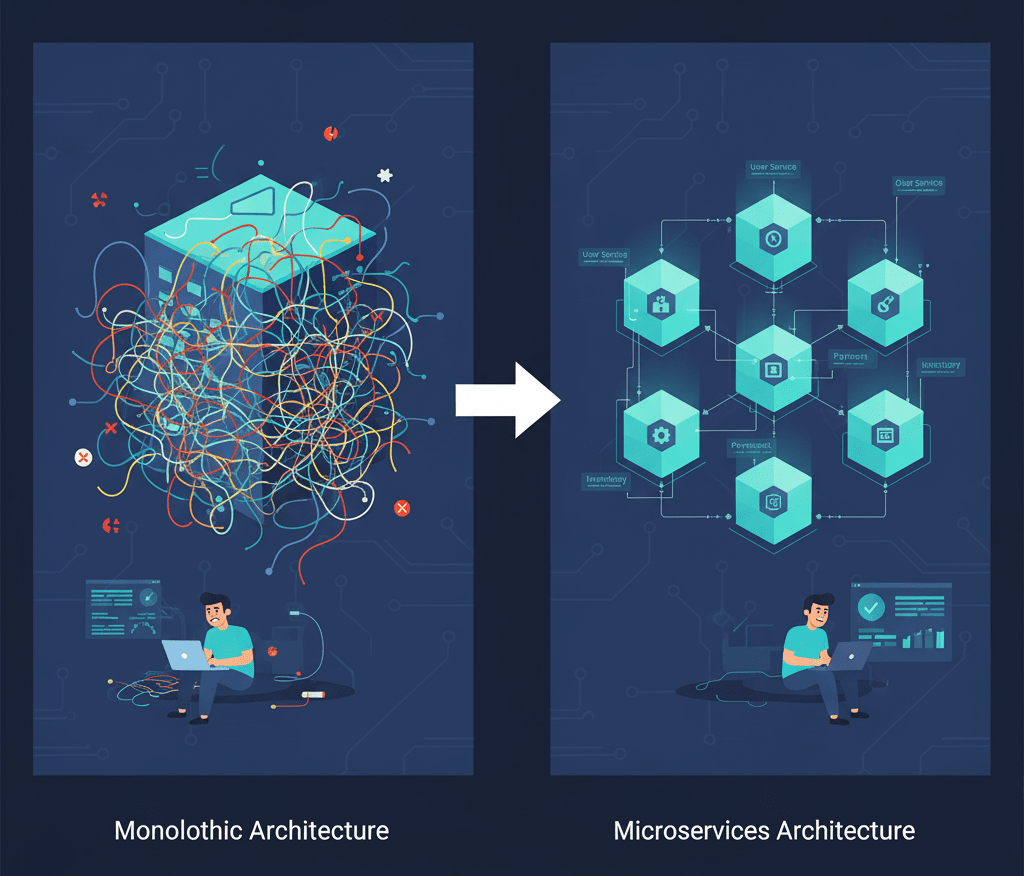
Microservices in Software Engineering
Microservices in software development/engineering is an architectural technique in which an application is built as a collection of small, independent services called microservices, each responsible for a specific business function. These services are loosely coupled, meaning they can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. The microservices architecture contrasts with monolithic architectures, where all functionalities are bundled into a single, large application.
Features of Microservices
Here are the key features of microservices:
- Independent Services: A microservice performs a specific task or business function. Hence, each microservice is an independent service.
- Loose Coupling: Services communicate with each other using well-defined application programming interfaces (APIs) and have negligible dependence on each other. They are loosely coupled.
- Independent Deployment: Each microservice can be deployed and updated independently without affecting the entire application.
- Scalability: Microservices can be scaled independently depending on specific requirements, thus optimizing resource utilization.
- Technological Diversity: Best technology stack can be chosen for each service promoting technological diversity and fostering innovation and flexibility.
- Organizational Structure: A Small, autonomous team can develop and manage microservices. This promotes agility and faster development cycles.
Benefits and Challenges of Microservices
The following table summarizes the benefits and challenges of microservice architecture.
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Faster Development and Deployment: New features can be deployed quickly with independent services. Also, development cycles are faster. | Increased Complexity: As services increase, managing a distributed system can be complex. |
| Improved Scalability: Easy scalability of services optimizes resource utilization and cost. | Inter-service Communication: It is difficult to coordinate and achieve inter-service communication. |
| Increased Resilience: Because services are independent, the failure of one service does not bring down the entire application, which increases the application’s resilience. | Distributed Transactions: It may be a complex task to ensure consistency across multiple services. |
| Technological Flexibility: Developer teams can choose the technology for each service. This leads to flexibility and promotes innovation and efficiency. | Monitoring and Logging: Monitoring and logging of microservices working is a challenge in a complex distributed environment. |
| Easier Maintenance and Updates: As services are independent, they are easy to maintain and update. It also reduces the risk of breaking the entire application. |
In essence, microservices architecture is an approach to building modern, scalable, and resilient applications by breaking down large applications into smaller, independent components.
Top 30 Microservices Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is Microservices Architecture?
Answer: Microservices architecture is a design pattern in which an application consists of a collection of small, independent, loosely coupled services. Each service implements a specific business functionality and communicates over lightweight protocols like HTTP or messaging queues.
2. How is Microservices different from Monolithic Architecture?
Answer: Monolithic architecture is one single large application that is tightly coupled and hard to scale or deploy independently. Microservices, on the other hand, are a collection of small, independent services that are loosely coupled and easier to scale and deploy.
3. What are the key features of microservices architecture?
Answer:
Some of the key features of microservices architecture are:
- Decentralized governance: As microservices are independent and loosely coupled, they can be developed and maintained in a decentralized manner
- Componentization: Each service in a microservice architecture is a component
- Flexibility in technology: Services can use different tech stacks as per their requirements
- Scalability: Services can scale independently
- Resilience: Faults and errors are isolated and do not affect other services
4. What are the main benefits of Microservices?
Answer: The benefits of microservices are:
- Scalability
- Independent deployments
- Improved fault isolation
- Technology diversity
- Easier to understand and modify small services
5. What challenges arise with Microservices?
Answer: Microservices face several challenges as follows:
- Complex deployments
- Network latency and reliability
- Distributed data management
- Service discovery
- Monitoring and logging
6. How do Microservices communicate with each other?
Answer: In microservice architecture, each of the independent service communicate with each other through:
- Synchronous protocols like HTTP/REST, gRPC
- Asynchronous via message brokers like RabbitMQ, Kafka, or JMS
7. What is a Service Registry?
Answer: A service registry is a central directory where microservices register themselves so others can find them. Example tools: Eureka, Consul, Zookeeper.
8. What is Service Discovery?
Answer: A technique or mechanism by which a microservice is located on a network is called Service Discovery. There are two types of service discovery techniques:
- Client-side (e.g., Netflix Eureka)
- Server-side (e.g., AWS ALB, Kubernetes)
9. How is data managed in Microservices?
Answer:
In microservice architecture, each service has its own database to ensure loose coupling and autonomy for each service. They do not depend on each other for data management.
10. What is eventual consistency?
Answer: Eventual consistency is a situation wherein services may not reflect changes or updates immediately but they become consistent over time. This is due to decentralized data management in microservices.
11. What is the Circuit Breaker pattern?
Answer: A circuit breaker pattern in microservices prevents a service from repeatedly calling a failing service. When failures reach a threshold, the circuit opens up and stops traffic temporarily.
Examples: Netflix Hystrix, Resilience4j.
12. What is the API Gateway pattern?
Answer: An API gateway is a single entry point for clients that routes requests to the correct microservice. Responsibilities of the API gateway include:
- Routing requests to appropriate services
- Authentication and authorization
- Caching and Monitoring
- Load Balancing
Tools: Kong, Zuul, NGINX, Spring Cloud Gateway
13. How do you handle transactions across multiple services?
Answer: Transactions across multiple services are handled in two ways:
- Two-phase commit (2PC) (not recommended for large-scale)
- Saga Pattern: local transactions with compensating actions for rollback
14. What are Sagas in Microservices?
Answer: Sagas are a sequence of local transactions in microservices and are a way of handling transactions. If one transaction fails, the saga executes compensating transactions to undo previous ones.
15. How do you test Microservices?
Answer: Microservices are tested in the following ways:
- Unit Testing of each service
- Contract Testing: done for validating APIs (e.g., Pact)
- Integration Testing: across services
- End-to-End Testing
16. What is containerization, and why is it essential for Microservices?
Answer: Each independent service can be packages as a container (e.g. Docker). It enables consistent environment and easy deployment of services.
17. How are microservices deployed?
Answer: Microservices are deployed using either of the following methods:
- Containers (Docker)
- Orchestration (Kubernetes)
- CI/CD pipelines (Jenkins, GitLab CI)
18. What is the Sidecar Pattern?
Answer: Sidecar pattern is basically a helper component for functions such as logging, monitoring etc. that are deployed alongside each microservices in the same container pod.
Common in service meshes like Istio.
19. How can Microservices be monitored?
Answer: Microservices can be monitored using tools like:
- Prometheus + Grafana
- ELK Stack
- Jaeger for tracing
- Zipkin
They can also be monitored using metrics such as CPU, memory, request latency, and error rates.
20. What is a service mesh?
Answer: A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer for managing service-to-service communication, security, and observability.
Examples: Istio, Linkerd
21. How do you secure Microservices?
Answer: Microservices are secured through:
- API Gateways that act as a single entry point
- OAuth2 / JWT for auth
- TLS for transport security
- Role-based access
22. What is Domain-Driven Design (DDD)?
Answer: DDD is a method of structuring microservices around business domains and subdomains (bounded contexts).
23. What are bounded contexts?
Answer: Each microservice owns its bounded context, which is a boundary within which a particular domain model is defined and applicable.
24. What’s the difference between orchestration and choreography?
Answer: Orchestration is a central controller that dictates the interaction between services. Choreography is how services react to events independently.
25. How does versioning work in Microservices?
Answer: Microservices versioning is done through:
- URI versioning (e.g., /v1/orders)
- Header-based
- Maintain backward compatibility
26. What tools are commonly used in Microservices architecture?
Answer: Some of the common tools used in microservices architecture are:
- Service Discovery: Eureka, Consul
- API Gateway: Zuul, Kong
- Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana
- Tracing: Jaeger, Zipkin
- Messaging: Kafka, RabbitMQ
- Deployment: Docker, Kubernetes
27. Name some famous companies that use Microservice architecture.
Answer: Microservices architecture has replaced monolithic architecture for most large-scale websites, like:
- Netflix
- Amazon, etc.
28. How do you ensure fault tolerance in microservices?
Answer: Fault tolerance in microservices is achieved through:
- Retry mechanisms: Retrying failed calls
- Circuit breakers: Using libraries like Hystrix, Resilience4j
- Fallbacks: Provide default responses
29. How do you handle data sharing between microservices?
Answer: Data sharing between microservices is handled using:
- Database per service: Each service has its own database
- Event-driven communication: Events are used to share updates
- API queries: Services expose read-only APIs
30. What are anti-patterns in microservices?
Answer: Microservices anti-patterns are flawed approaches to designing and implementing microservices. Anti-patterns often appear beneficial initially, but can lead to significant problems like reduced scalability, performance bottlenecks, and increased complexity. The following are some common anti-patterns:
- Shared database: Coupling between services
- Over-engineering: Adding microservices unnecessarily
- Too fine-grained services: Leads to performance issues
Conclusion
The software development environment is evolving at a neckbreak speed as a result of innovation in microservices architecture for contemporary applications. Understaindng the basic concepts and challenges in microservices is crucial for success, for both candidates as well as hiring managers.
Microservices are the future of software development with limitless potential. Hiring experienced microservices engineers to advance your organization is of prime importance.
|
|
